How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a question many aspiring pilots ask. This guide provides a comprehensive overview, from understanding basic drone components and pre-flight checks to mastering flight controls and capturing stunning aerial footage. We’ll cover essential safety procedures, legal considerations, and troubleshooting common issues, equipping you with the knowledge to confidently take to the skies.
We’ll delve into the intricacies of drone technology, explaining the functions of various components like propellers, motors, and flight controllers. You’ll learn about different battery types and their impact on flight time, as well as mastering essential maneuvers like takeoff, landing, and precise directional control. Beyond the basics, we’ll explore advanced features like flight modes and camera settings to help you capture professional-quality aerial photography and videography.
Finally, we’ll address important safety regulations and maintenance practices to ensure the longevity of your drone.
Drone Components and Terminology
Understanding the various components of a drone and their functions is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section provides a breakdown of key components and defines common drone terminology.
Drone Component Functions
A drone comprises several essential components working in unison. These include:
- Propellers: These rotating blades generate the thrust necessary for flight. Different propeller designs offer varying levels of thrust and efficiency.
- Motors: Electric motors power the propellers, converting electrical energy into rotational motion. Brushless motors are common in modern drones due to their efficiency and longevity.
- Flight Controller: The brain of the drone, this component receives input from sensors and the remote controller to regulate motor speeds and maintain stability. It utilizes gyroscopes, accelerometers, and barometers to accurately determine the drone’s position and orientation.
- Battery: Provides the power to the drone’s components. The flight time is directly related to the battery capacity and the drone’s power consumption.
- Camera: Captures photos and videos. Features vary widely, from basic HD cameras to high-resolution models with advanced features like gimbal stabilization.
- GPS Module (optional): Allows the drone to pinpoint its location, enabling features like GPS-assisted flight modes and return-to-home functionality.
- Radio Transmitter/Remote Controller: Allows the pilot to control the drone’s movement and camera functions.
Drone Terminology Glossary

Familiarizing yourself with common drone terms is essential for understanding operation manuals and online resources.
- Altitude Hold: Maintains a constant altitude.
- Gimbal: A stabilized mount for the camera, minimizing vibrations and ensuring smooth footage.
- Return-to-Home (RTH): An automated function that guides the drone back to its takeoff point.
- Failsafe: A safety mechanism that takes over if communication with the drone is lost.
- LiPo Battery: Lithium Polymer battery, a common type of rechargeable battery used in drones.
- mAh (milliampere-hour): A measure of battery capacity, indicating how long the battery can power the drone.
- ESC (Electronic Speed Controller): Regulates the speed of each motor.
Drone Battery Comparison
Different battery types offer varying performance characteristics.
| Battery Type | Voltage (V) | Typical Capacity (mAh) | Approximate Flight Time (minutes) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LiPo | 11.1 – 22.2 | 1500 – 5000 | 15-30 |
| LiHV | 11.1 – 22.2 | 1500 – 5000 | 15-35 |
| LiFePo4 | 12.6 – 25.2 | 1500-5000 | 15-30 |
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist is paramount for safe and legal drone operation. This section Artikels essential checks and procedures.
Pre-Flight Checklist
Before each flight, meticulously perform the following checks:
- Inspect propellers for damage or cracks.
- Visually examine motors for any signs of wear or damage.
- Check battery level and ensure it’s fully charged.
- Verify GPS signal strength (if applicable).
- Review local regulations and airspace restrictions.
- Confirm that all necessary safety features are enabled.
- Select a suitable takeoff and landing location.
Pre-Flight Inspection Flowchart
A visual representation of the pre-flight inspection process helps streamline the process and minimize errors.
The flowchart would start with “Begin Inspection” and branch into the propeller check, motor check, battery check, GPS signal check, and regulatory check. Each check would lead to either “Pass” or “Fail.” A “Fail” would result in repair or replacement, while multiple “Passes” lead to “Proceed to Flight.”
Taking Off and Landing
Proper takeoff and landing techniques are essential for safe drone operation, regardless of weather conditions.
Takeoff and Landing Techniques
Takeoff and landing procedures should adapt to environmental factors. In calm conditions, a gentle, controlled ascent and descent is sufficient. In windy conditions, it is crucial to account for wind direction and strength, performing a more controlled and deliberate maneuver. Assisted takeoff modes can help in challenging conditions.
Takeoff and Landing Location Selection
Choose a level, open area free from obstacles. Avoid areas with tall structures, power lines, or bodies of water. Consider wind direction and strength when selecting a landing spot. Ensure you have sufficient visibility.
Takeoff and Landing Methods
Assisted takeoff utilizes the drone’s internal systems to aid in a smoother, more controlled launch. Manual takeoff provides more direct control but requires more skill.
Controlling Drone Movement
Understanding the functions of the remote controller is crucial for precise drone manipulation.
Remote Controller Functions
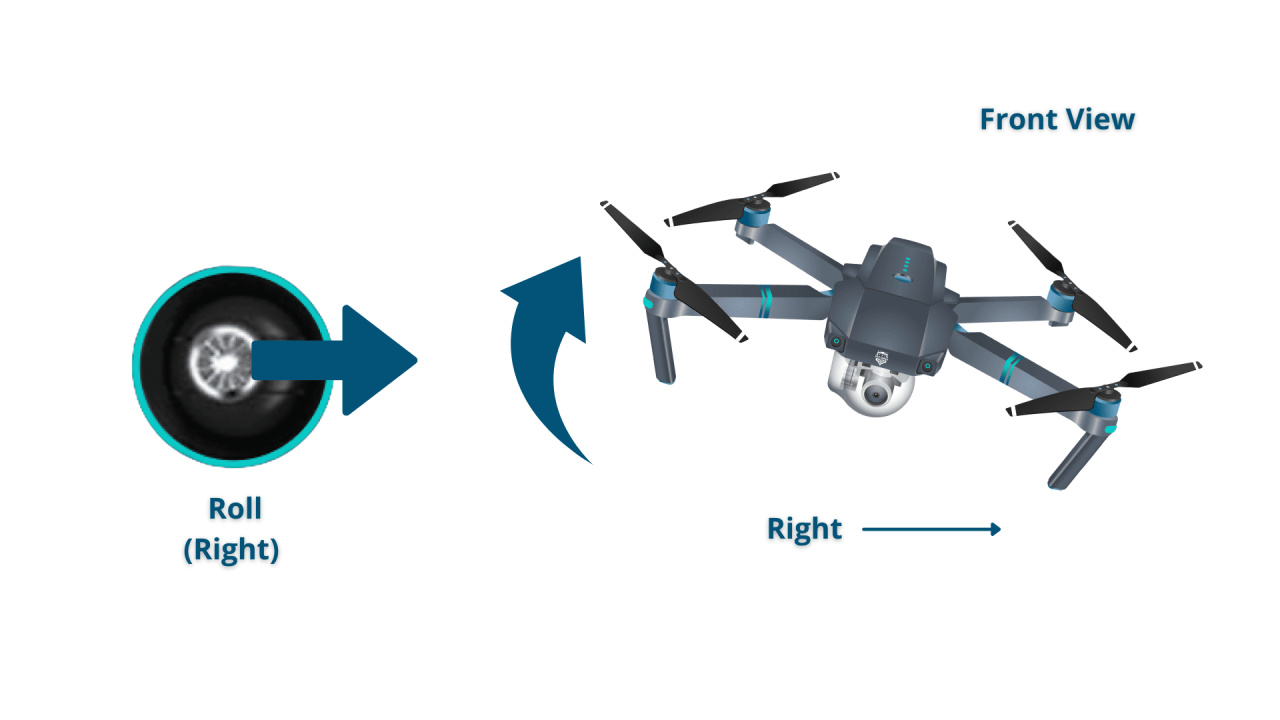
Most drone remotes feature two joysticks for controlling pitch, roll, yaw, and throttle. Buttons typically control camera functions, return-to-home, and other features.
Basic Drone Maneuvers
Step-by-step instructions for basic maneuvers:
- Ascending: Gently push the right joystick upwards.
- Descending: Gently push the right joystick downwards.
- Moving Laterally: Push the left joystick left or right to move the drone sideways.
- Rotating: Rotate the left joystick to spin the drone clockwise or counter-clockwise.
Control Stick Inputs and Drone Movement, How to operate a drone
| Control Stick | Movement | Direction |
|---|---|---|
| Left Joystick (Horizontal) | Lateral Movement | Left/Right |
| Left Joystick (Vertical) | Yaw (Rotation) | Clockwise/Counter-clockwise |
| Right Joystick (Vertical) | Ascent/Descent | Up/Down |
| Right Joystick (Horizontal) | Pitch/Roll | Forward/Backward, Left/Right Tilt |
Camera Operation and Image Capture
Understanding camera settings and techniques is key to capturing high-quality aerial media.
Drone Camera Settings
Typical settings include resolution (e.g., 4K, 1080p), frame rate (e.g., 24fps, 30fps, 60fps), video bitrate, and various image settings (ISO, shutter speed, aperture, white balance – where applicable).
Tips for High-Quality Aerial Media
Tips include choosing optimal lighting conditions, maintaining stable flight, experimenting with different angles, and utilizing post-processing techniques.
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. A crucial aspect is learning the basics of controlling the drone itself, which you can find comprehensively explained at how to operate a drone. Once you’ve grasped these fundamentals, practicing in a safe, open area will build your confidence and proficiency in operating a drone effectively and responsibly.
Common Camera Problems and Solutions

Common issues include blurry footage (adjusting settings, stabilizing the drone), overexposed images (adjusting ISO and shutter speed), and poor image quality (cleaning the lens).
Flight Modes and Features
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and automation.
Flight Mode Descriptions
GPS mode utilizes GPS signals for precise positioning, attitude mode relies on onboard sensors for stability, and sport mode allows for more agile and responsive maneuvers.
Flight Mode Benefits and Limitations
GPS mode offers stability but can be affected by GPS signal loss. Attitude mode is suitable for close-range maneuvers but lacks precision without GPS. Sport mode provides responsiveness but demands greater piloting skill.
Advanced Drone Features
Advanced features such as “Follow Me,” “Point of Interest,” and waypoint navigation enhance functionality and offer automated flight capabilities.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Mastering these skills ensures safe and efficient drone operation, ultimately leading to a more enjoyable experience.
Safety and Legal Considerations
Adhering to regulations and safety protocols is paramount for responsible drone operation.
Drone Regulations and Airspace Restrictions
It’s crucial to understand and comply with all local, state, and federal drone regulations, including airspace restrictions near airports and other sensitive areas.
Safe Operating Distances
Maintain safe distances from people, property, and obstacles. Avoid flying over crowds or sensitive areas. Always be aware of your surroundings.
Safe Flight Zone Illustration
A safe flight zone would be depicted as a circular area with the drone at the center. Obstacles (trees, buildings) would be represented outside the circle, while people would be kept a significant distance away, also outside the circle. The size of the circle represents the operational radius, adjusted based on the drone’s capabilities and environmental conditions.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
This section provides solutions for common drone problems.
Troubleshooting Guide
- Low Battery: Charge the battery fully.
- GPS Signal Loss: Fly in an open area with a clear view of the sky.
- Motor Malfunctions: Inspect motors for damage; consider replacing faulty components.
- Drone unresponsive: Check battery level, signal strength, and remote control connectivity. Try restarting the drone and the remote.
Common Error Codes and Meanings
| Error Code | Meaning | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Error 1 | Low Battery | Charge the battery |
| Error 2 | GPS Signal Lost | Fly in an open area |
| Error 3 | Motor Failure | Inspect and/or replace the motor |
Drone Maintenance and Storage: How To Operate A Drone
Regular maintenance extends the lifespan of your drone.
Routine Maintenance Schedule
Clean the drone after each flight, inspect components for damage, and lubricate moving parts as needed. Regularly check and calibrate sensors.
Extending Drone Lifespan
Proper storage, avoiding extreme temperatures and humidity, and using high-quality batteries contribute to longevity.
Drone Storage Checklist
- Store the drone in a cool, dry place.
- Protect the drone from dust and debris.
- Store batteries separately in a designated storage case.
- Ensure all components are clean and dry.
Mastering the art of drone operation requires a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical application. This guide has equipped you with the fundamental understanding needed to safely and effectively pilot your drone, capture breathtaking aerial visuals, and navigate the legal and technical aspects of this exciting technology. Remember to always prioritize safety, adhere to regulations, and continue practicing to hone your skills.
The skies await!
FAQ Section
What is the best type of drone for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS and assisted flight modes are ideal for beginners. Research models known for their stability and ease of use.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Compass calibration is recommended before each flight, especially if you’ve flown near magnetic interference.
What should I do if my drone loses GPS signal?
If GPS is lost, immediately switch to a lower altitude and attempt to regain signal. If unsuccessful, execute a safe landing.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Flight time varies greatly depending on the drone model, battery size, and flight conditions. Consult your drone’s specifications for estimated flight times.
